Permanent Maxillary Central Incisor
There are 4 permanent maxillary incisors ,2 in each quadrants.The incisors adjacent with the midline of the jaw are known as central incisors.
Maxillary and Manndibular central incisors are the only neighbouring teeth with mesial side is in contact with each other. The central incisors are the anterior most teeth with widest mesio diatlal length.It is also featured with nearly sharp incisal edge , straight mesial outline along with sharp mesio incisal angle and slight convex labial surface.All these features gives the teeth a squarish or rectangle appearence. The lingual surface is comparatively concave with more irregularity and a prominant cingulum.
Central incisors are generally associated with cutting and shearing of food during mastication. The functions of the maxillary central incisors are not only limited to mastication, As their shape size colour and placements contribute to someone`s natural appearence and esthetics. Also helps in talking.
Tooth notation
universal right 8 left 9
F.D.I right 11 left 21
Chronology of Maxillary Central Incisor
eruption= 7-8 years
root completion= 10 years
dimensions
cervico-incisal length of crown= 10.5mm
mesio-distal diameter of crown= 8.5mm
mesio-distal diameter at cervix= 7mm
labio-lingual diameter of crown= 7mm
labio-lingual diameter at cervix= 6mm
curavture of cervical line(mesial)= 3.5mm
curvature of cervical line(distal)= 2.5mm
These are general dimensios, however every indivisual have some variations.
Maxillary Central Incisor Anatomy
A detailed anatomy of a tooth is typically examined through five key aspects.
Labial Aspect
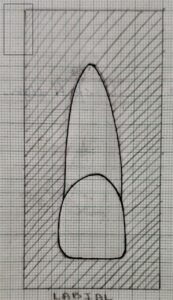
- It is the outer or facial aspect of the tooth.Labial aspect of a central incisor appears quite rectangular with the surface slightly convex and smooth.From this view the mesial, distal outlines , incisal edge and incisal line angles are greatly appreciated.
- Generally, the crown of an average central incisor measures from 10 to 11 mm.The mesio-distal length is greater at the incisal one-third measuring upto 8-9mm.whereas the length deacreases at the cervical one third .
- The mesial outline of the central incisor is straight or slightly convex with a sharp mesio-incial angle. A line drawn through the center of the root and crown of the maxillary central incisor tends to be parallel with the mesial outline of the crown and root.the contact area is located near junction of middle and incisal one-third.
- The distal outline of the crown is more rounded with a rounder disto-incisal angle .The contact area is located in the middle-third closer to the cervical line.
- the cervical outline of the crown forms a semicircular curve, extending towards root.
- The incisal edge of a newly erupted central incisor features prominant mamelons.Once the tooth has been functioning long enough the incisal edge becomes smooth .
- The root tapers toward the apex giving a conical appearence, with a blunt apex.Typically the root is 2 to 3 mm longer the crown.
Lingual Aspect
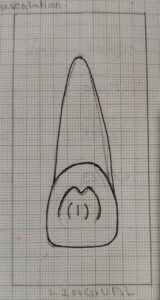
- Unlike the labial surface, the lingual surface of the maxillary ceentral incisor is marked with irregular concavities and convexities.
- Just below the cervical line a smooth convexity is present, this is called the cingulum.
- Along with the mesial and distal outline the marginal ridges are present, which are continious with the cingulum.
- Below cingulum and in between the marginal ridges a shallow concavity is present; that is the lingual fossae it is inverted w shaped in maxillary cnetral incisor.The lingual fossa is bounded mesio-distally by the corresponding marginal ridges and incisally by the lingual portion of incisal ridge.
- Typically there are developemental grooves extending from the cingulum into the lingual fossa.
- Both the crown and root tapers lingually.They are narrower when observed from the lingual aspect.
Mesial Aspect
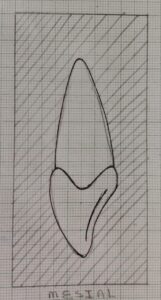
- This is the sidewise view which is adjacent to the midline.
- The crown appears wedge shaped, or triangular with apex directed towards incisal edge.
- The incisal ridge is aligned with the line bisecting the tooth.
- The crest of curvature is present on the cervical third of the crown just below the cervical line, occuring due to the convexity of the labial outline and cingulum present on the lingual surface.
- The root is conical from the mesial aspect with a blunt or roundec apex.
- The contact point is located on its incisal third.
Distal Aspect
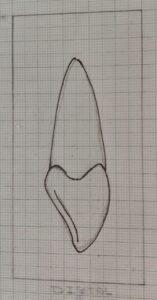
- The distal aspect is almost similar except for some little variations.As the crown appears shorter than mesial aspect due to shorter cervico incisal length.
- The crown appears thicker in the incisal third.This appears due to labial outline is more inclined toward lingual from the distal side.
- The crest of curvature is less than that of the mesial aspect.
- Because at the distal side the tooth contacts with the lateral incisor the contact point is at a higher level than the mesial near the junction of incisal and middle third.
Incisal Aspect
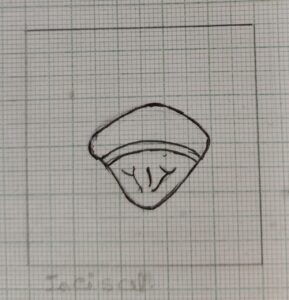
- For maxillary central incisor incisal aspect the crown appears rouhly triangular.
- the root is not seen from this aspect, because the crown is superimposed over the root.
- The dimensional difference of the labial and lingual aspect is prominant from this aspect. The labial aspect is broader and convex and the lingual aspect appears shorter and it tapers lingually toward the cingulum.
- The incisal ridge is clearly visible.
- The mesiolabial and distolabial line angles are are prominant.
DISORDERS
1.Malocclusion-crowding, spacing, overjet, over bite can hamper the normal alignment of permanent maxillary central incisors .
it can occur due to genetics, thuumb sucking, pacifier use etc.
treated through orthodontic procedures as braces aaligners etc.
2.discolouration-Intrinsic discoloration can occur due to trauma or developemental issues.Extrinsic discloration occurs due to dietry components.
3.Caries-Decay can occur due to poor oral hygiene or high sugar intake .
treatment; fillings, crowns and root canal treatemnt in severe cases.
4.peg shaped incisors- In this case the crown of incisor rather than having a flat incisal edge is shaped like a cusp or canine .
5.gemination- When a single tooth bud starts to devides and forms a enlarged bifit tooth.
6.fusion- Two crown of other tooth gets united in this case.
associated
7.Solitary Median Maxillary Central Incisor [SMMCI]-It a rare developemantal anomaly where instead of a pair only a single maxillary central incisor is present in the upper jaw at the midline. It can occur in primary as well as permanent dentition. it may be associated with mutation in genetical components such as SHH.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the length of maxillary central incisor ?
A: The average length of maxillary central incisor is 23-24 mm, the crown of permanent maxillary central incisor is 10.5mm and the length of root is 13 mm
Q:What is the Chronology of maxillary central incisor ?
A: time of eruption is 7 to 8 years
root completion occurs at an age of 10 years.
Q: What is the tooth number of the maxillary central incisor ?
A: universal right= 8 left= 9
FDI right= 11 left= 21
Q: How would you describe the incisal aspect of maxillary central incisor ?
A: The description of maxillary central incisor-It is broad and relatively flat giving a chisel-like appearance. it has a triangular shape when viewed from above. The incisal edge is straight in newly erupted teeth it may contain slight ridges called mamelons. The mesio-distal length is wider than labio-lingual dimension.The lingual aspect shows convexity due to the presence of the cingulum.